BREAST SURGERY
Breast reconstruction
What is that?
Breast reconstruction is the group of surgical procedures that allow the reconstruction of the breast following a mastectomy. For every woman there is the right, personalized reconstruction technique: each case must be carefully analyzed and everything must be planned before the intervention with the patient: the patient who has to face the breast reconstruction process must do it with the utmost awareness.
Which techniques are included?
There are numerous techniques, which we will list in this article: in principle there are two lines of thought: you can use the prosthesis or the autologous tissue, that is, taken from the patient herself. Breast cancer affects one in eight women, and only one in eight undergoes breast reconstruction. A woman operated on for cancer must be adequately informed before starting the destructive therapeutic process: awareness must be increased. Medical information is essential in this. Thanks to a constant increase in access to information through the mass media, the number of women who will undergo breast reconstruction is constantly increasing.
What are we talking about?
Various types of oncological surgery can be performed: there can be conservative surgery, when possible and when local conditions allow it, which respects the breast and which sometimes subsequently needs radiotherapy, and there are more demolishing operations: the mastectomy that removes the entire gland and needs reconstruction by the plastic surgeon. There are mastectomies that spare a large part of the skin. This simplifies the reconstruction. Major plastic reconstructions are instead reserved for cases in which the oncological removal was more important. Selected patients can undergo immediate reconstruction: at the end of the demolition performed by the general breast surgeon, the plastic surgeon performs the reconstruction.
As we said, there are two different ways of acting
- Use of prostheses: in selected patients: thin patient. These are the techniques with the least surgical invasiveness
- Use of own tissues, especially from the belly: reconstruction works very well in selected patients (DIEP intervention) are the most sophisticated techniques.
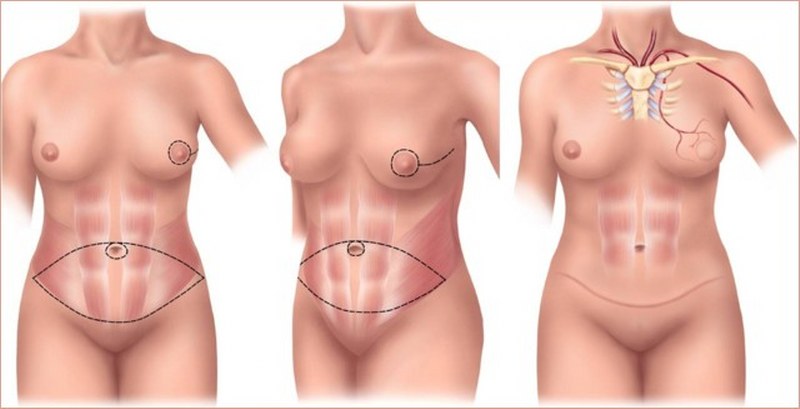
The customization of breast reconstruction is a basic concept. In recent years there has been an evolution in techniques.
Post quadrantectomy breast reconstruction
Following a conservative intervention, such as quadrantectomy: a remodeling of the mammary gland is performed, through the use of local flaps. It is possible to intervene in the contralateral breast, through the so-called mastopexy / reduction or with the insertion of breast implants (breast augmentation).
BREAST SURGERY
Are you interested in breast surgery?
Traditional post mastectomy breast reconstruction
With prosthesis, immediate or deferred
The insertion of the prosthesis can take place simultaneously with the removal of the tumor, if local conditions allow it. Otherwise, at the same time as the demolition operation, a breast expander is inserted, or an expandable prosthesis with physiological solution, partially inflated during the operation. About three weeks after surgery, expansion begins in the clinic, gradually inflating the expander every 15 days so that the tissues react gradually. At the end of the expansion, which takes place in about 2/3 months, we keep the expander in place. This is replaced in a subsequent surgery with a definitive prosthesis.
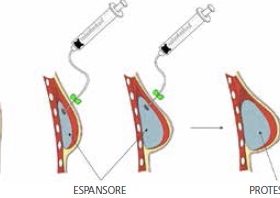
The breast expander is a temporary prosthesis which is subsequently replaced by a definitive prosthesis..
It should be emphasized that at any time the patient can decide to put on a prosthesis: in fact, sometimes the patient refuses to put on the prosthesis during the surgery to remove the tumor, for example out of fear. The patient can change her mind even years later and therefore proceed with the definitive reconstruction.
Breast reconstruction with own tissues (autologous)
These techniques use the tissues of the patients themselves: most of the time the donor site is the abdomen of the patients themselves, from where a pedunculated flap (i.e. with its own vessels that are rotated (TRAM flap) or a flap with its own vessels can be taken. which are sutured with microsurgery techniques in the operating room (so-called DIEP flap). These techniques are more sophisticated and complicated, but they cannot be proposed to all patients: the patient, moreover, the operation is much longer 5/6 hours and predicts slower recovery after surgery.
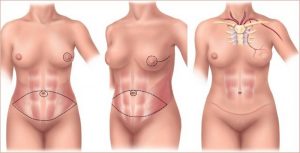
The abdomen is the ideal site for the flap used for breast reconstruction in selected patients.
The synergy between the different disciplines between the breast specialist and the reconstructive plastic surgeon makes the patient involved in decisions, with positive spirit. This helps her in the evolution of the disease. The checks following the reconstruction surgery are clear: the prosthesis does not alter the ability to control the breast. Many women in Italy and around the world wear prostheses, both additive and in reconstruction, after removal of breast cancer. Women with implants compared to reconstructive patients sometimes feel exempt from having breast investigations: in reality it is women who need to do more control.
Nipple sparing mastectomy
This technique is provided when the NAC (nipple areola complex / nipple areola complex) is not affected by the disease: it involves the removal of only the mammary gland without removing the skin of the nipple and making reconstruction easier.
Lipofilling
In recent years, fat has emerged as an important resource. Adipose tissue, in fact, can be used as a filler (etymologically lipos: fat to fill: to fill). The fat, after being aspirated with special cannulae, is purified and separated from the liquid component. In this way a fluid substance is obtained, with a certain viscosity, ideal for being injected with thin cannulae in the areas to be treated.
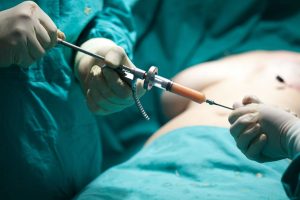
The moment of the removal of the adipose tissue from the patient.
Also in this case, it is an autologous tissue, as it is produced by the patient herself, with no possible complications other than partial resorption. However, at least 5/6 interventions are required before obtaining a valid result. In motivated and selected patients it can therefore be proposed as a valid therapeutic option.